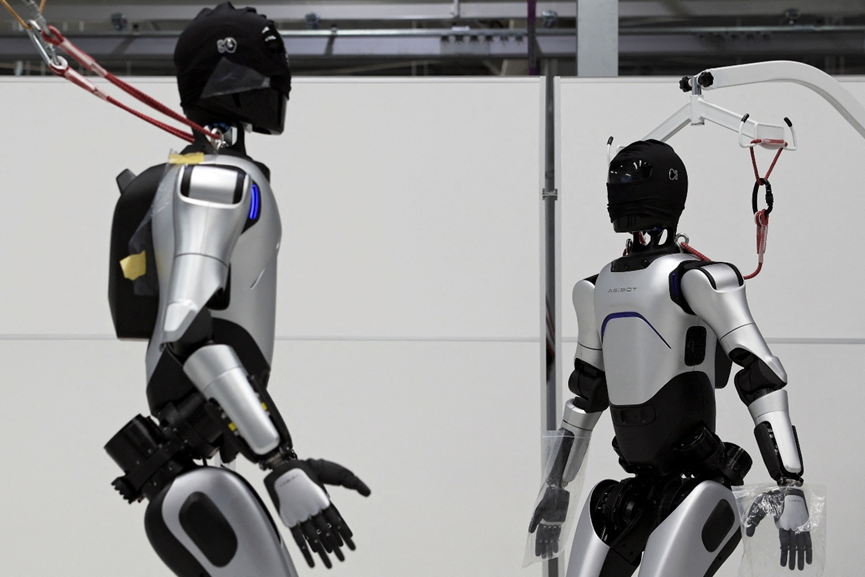
A humanoid robot from the AgiBot factory in Shanghai, China.
Image source: Reuters/Florence Lo
Keman
SAP Global Senior Vice President
By 2040, billions of humanoid robots could be deployed worldwide, with their applications extending far beyond today's factory robots.
These robots are poised to revolutionize multiple fields, including healthcare, public space maintenance, retail services, and personal assistance.
Both businesses and individuals can benefit from humanoid robots, but embracing this transformation requires establishing clear safeguard mechanisms.
In 2017, Google’s AlphaGo system defeated the world’s top Go player, Ke Jie, sparking a global conversation about AI’s cognitive capabilities. More recently, at Beijing’s Half Marathon, humanoid robots competed directly against humans on the same course, marking a groundbreaking new milestone.
Early robot prototypes were limited to controlled demonstrations, but this competition—featuring 21 humanoid robots completing a 21-kilometer (13-mile) race—highlights how they are increasingly becoming integrated into human environments.
This evolution mirrors the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), which have already shaken up traditional automotive powerhouses like Germany. So, could humanoid robots also redefine global markets and industrial ecosystems?
How humanoid robots are transforming industries
As the name suggests, a humanoid robot is a type of robot that resembles humans in appearance and can mimic human movements. As a specialized service robot, it was originally designed to work alongside humans, enhancing productivity across a variety of settings.
Leveraging advanced AI technology, these robots can perceive their surroundings, make decisions, plan actions, and autonomously execute complex tasks. Thanks to their rapid learning and adaptability, humanoid robots are evolving at an unprecedented pace.
Analysts predict that humanoid robots are poised to become a common sight in our daily lives within the next decade. By 2040, it’s estimated that billions of humanoid robots will be deployed worldwide, operating across a far broader range of applications than today’s factory robots—spanning healthcare, public space maintenance, retail services, and even personal assistant roles.
Goldman Sachs predicts that the humanoid robot market could reach $38 billion by 2035, while Fortune Business Insights forecasts the market to grow at nearly 50% annually, expanding to $66 billion by 2032.
The versatility of humanoid robots relies on a complex, cross-industry supply chain that spans semiconductors, AI systems, actuators (which convert energy into motion or force), and sensors. These robots require a significant number of high-performance chips for motion control, perception, and decision-making—meaning that as the market for humanoid robots expands, the semiconductor industry will experience unprecedented growth.
Meanwhile, advancements in AI technology have already propelled humanoid robots from the lab into the marketplace, capturing widespread attention within the tech community. Breakthrough projects such as Tesla’s Optimus, Figure AI backed by OpenAI, and Unitree Technology’s humanoid robots are accelerating efforts toward commercialization and large-scale production, bringing machines once thought to exist only in science fiction closer than ever to everyday reality.
As humanoid robots become increasingly prevalent in everyday life, the global labor market will face a landscape of both challenges and opportunities. Society will need to develop new policies and address their ethical and economic implications. This rapidly advancing technology, therefore, heralds an exciting yet complex future—where expanding application scenarios will drive significant market growth.
While some worry about job displacement and over-reliance on technology, workers will also benefit. Enhancing human capabilities can make jobs more fulfilling and productive, while robots take on riskier tasks, ultimately improving workplace safety.
Additionally, businesses can also expect to enhance customer experiences as a result, while simultaneously creating new roles—such as robotics training, monitoring, and collaboration—that will ensure humans remain at the heart of the future workforce.
Global humanoid robot competition intensifies
Breakthrough advancements in generative AI have dramatically accelerated the development of humanoid robots, and this momentum shows no sign of slowing down. In this global race, Chinese and U.S. companies are at the forefront, driving innovation in both the AI market and the field of humanoid robotics.
According to the Stanford AI Index Report, 83% of AI-related intellectual property and 90% of prominent foundational models originate from China and the United States, with France ranking third at 5%. This includes large language models, reinforcement learning, neural networks, and thousands of sensors—further highlighting that the development of such advanced robotics is almost entirely concentrated in either China or the U.S.
In this transformative field, competition between China and the U.S. is fierce, with China's rapid rise particularly striking. Market forecasts highlight this growing trend: China's humanoid robot market is expected to surge from 2.76 billion RMB (about $377.56 million) in 2024 to 75 billion RMB (roughly $10.26 billion) by 2029.
This will capture nearly one-third (32.7%) of the global market, solidifying China's position as a global leader. This growth is driven by the government's supportive policies, world-class infrastructure, and its undisputed leadership in patent applications—over the past five years, China has already registered 5,688 humanoid robot patents, nearly four times the total number filed by the United States (1,483 patents).
Recent advancements in humanoid robot development, such as China's marathon-running robot, demonstrate that the country isn’t just joining the race—it’s setting the pace on this trillion-dollar technology track, once again reshaping the global industry landscape. Beyond pioneering new frontiers, China is also challenging the dominance of industrial powerhouses like South Korea, Germany, and the United States in driving real-world applications.
The Future Path of Humanoid Robotics
Humanoid robots are poised to reshape the labor landscape across multiple industries. In hazardous industrial operations, robots can take on high-risk tasks, minimizing human exposure to dangerous environments and significantly reducing workplace injury rates.
Meanwhile, in sectors requiring meticulous, personalized services—such as elderly care and customer engagement—they offer a scalable solution to labor shortages while simultaneously delivering tailored companionship services. This dual capability is particularly crucial for countries like Germany, Japan, South Korea, and China, where rapid population aging is intensifying demographic pressures and exacerbating workforce challenges.
In the future, humanoid robot systems spanning multiple manufacturers and countries will achieve seamless interoperability within a unified operational environment, driving sustainable growth through a coordinated digital ecosystem.
Amazon's current deployment offers a glimpse into the future: 750,000 robots are already working collaboratively across nine specialized categories to support package fulfillment and delivery. Now, the company is pushing boundaries even further by piloting humanoid robots for last-mile delivery—deploying them alongside human drivers while simultaneously serving multiple addresses. Although the project remains in a controlled testing phase, its primary goal is to demonstrate that robots can handle real-world variables—and, in the short term, complement, rather than fully replace, human roles.
Seamless collaboration between robotic ecosystems isn’t just a matter of technical compatibility—it could also reshape how industries leverage global innovation. These interconnected systems are poised to lay the foundation for a new era, where AI-powered robotics become a widespread force in boosting productivity.
Humanoid robot development requires safety guard mechanisms.
However, we cannot ignore the challenges, which include privacy and data risks, reliability issues, the loss of job opportunities, and broader economic ripple effects.
More fundamentally, technology’s greatest promise lies in driving societal progress and enhancing human well-being—a commitment that is perfectly embodied in humanoid robotics. These technological marvels are already transforming industries across the board—from hazardous tasks in extreme environments and intimate roles within domestic settings, to seamless online delivery services.
However, society and the industry need clear safeguard mechanisms to embrace this transformation. Since humanoid robots are capable of moving independently in their environment, they must adhere to social norms, ensuring their behavior is safe, ethical, and predictable—especially in private, domestic spaces.
To avoid the catastrophic scenarios depicted in Hollywood and science fiction, fault-protection mechanisms are essential. Their implementation requires a multi-layered approach: engineers must design robust technical safeguards, companies need to enforce rigorous safety protocols, and governments should establish comprehensive regulatory frameworks. Ultimately, humans also need training on how to safely interact with and communicate effectively with humanoid robots.
Humanoid robots are no longer a concept of the future—they already exist and are set to have a profoundly transformative impact on society and industry. We shouldn’t merely remain passive observers; instead, we must learn to collaborate with them. Both businesses and individuals can reap significant benefits by integrating humanoid robots into production, services, professional fields, and even everyday life.

The above content represents the author's personal views only.This article is translated from the World Economic Forum's Agenda blog; the Chinese version is for reference purposes only.Feel free to share this in your WeChat Moments; please leave a comment at the end of the post or on our official account if you’d like to republish.
Translated by: Sun Qian | Edited by: Wang Can
The World Economic Forum is an independent and neutral platform dedicated to bringing together diverse perspectives to discuss critical global, regional, and industry-specific issues.
Follow us on Weibo, WeChat Video Accounts, Douyin, and Xiaohongshu!
"World Economic Forum"