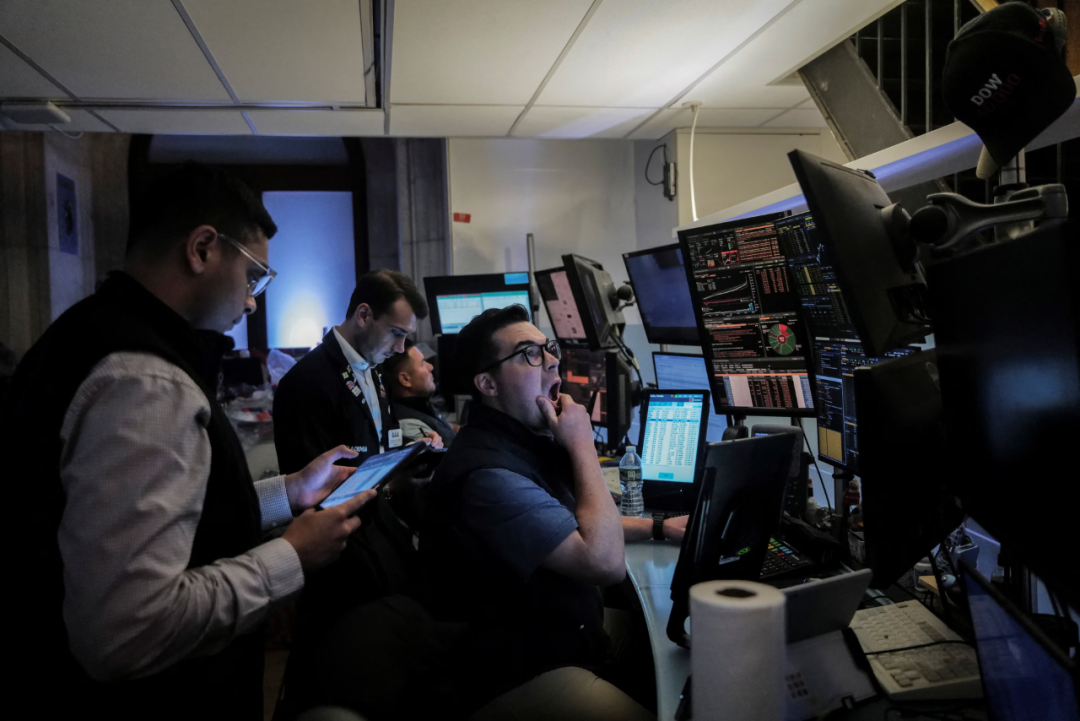
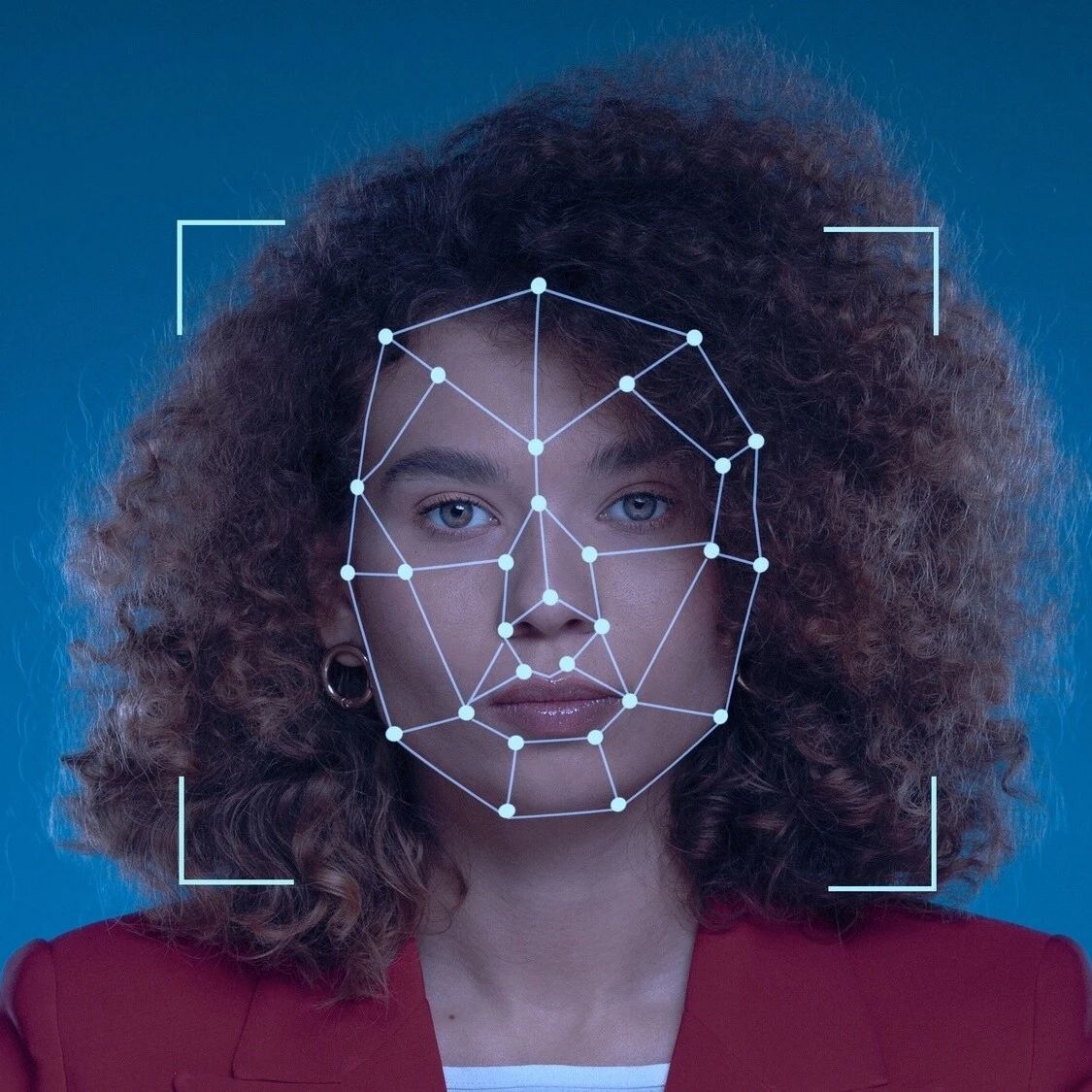
Data-intensive financial tasks are soon to be replaced by artificial intelligence.
Image source: Reuters/Jeenah Moon
Atul Kumar
Forum Agenda Writer
Data-intensive industries are most vulnerable to the impact of artificial intelligence.
Industries lacking data are rushing to go digital in order to reap the benefits of artificial intelligence—but this is leading to increased friction with established practices.
Employees and job seekers must focus on opportunities that combine technical expertise with human judgment and business needs.
Everyone is talking about AI taking over jobs, and to some extent, that’s true. We’re worried about AI stepping in to replace human work, but we don’t fully understand *how* it will happen, *when* it will occur, or how much time we actually have left to prepare.
Most people believe that the complexity of a task determines the pace of AI adoption. However, this assumption is entirely mistaken. As Sun Tzu once said, "Know yourself and know your enemy, and you will never be defeated in a hundred battles." You need to understand the following dynamics.
How Artificial Intelligence Works
Even for experts, the mechanisms of artificial intelligence remain somewhat unclear. Yet, one important thing we do know: AI learns.
Artificial intelligence models learn from data. A model with limited data is like a toddler taking its first wobbly steps; in contrast, an AI model equipped with vast amounts of data resembles a seasoned grandfather with decades of experience.
The Data Paradox
Which is harder—driving a car or writing code? Most people would say writing code. Yet, in the evolution of artificial intelligence, the situation seems to be the opposite.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are relatively new. Before the emergence of ChatGPT, few people associated artificial intelligence with chatbots—most would instead think of *The Terminator*. However, with the rise of neural networks like word2vec, the LLM era began roughly around 2013–2014. In contrast, autonomous driving dates back much earlier, to the 1980s. In 1987, Ernst Dickmanns’s team used computer vision technology to enable a Mercedes-Benz van to drive autonomously at 96 km/h on German highways.
Despite such a significant lead, autonomous driving still lags behind LLMs. While ChatGPT delivers consistent performance across countless scenarios, the AI-driven "driver" continues to show mixed results.
Why is that? Companies like Tesla and Waymo have already invested billions of dollars. Yet, if a new company wants to enter this field—even with top-notch engineers and unlimited funding—it would still need thousands of hours of diverse driving data. Some accident types are so rare that it’s virtually impossible to train AI systems using them.
Meanwhile, LLMs can be trained across the entire internet—a vast playground brimming with rich data. That’s why AI is more likely to replace programmers than drivers—not because coding is easier, but because the relevant data is far more accessible.
Overall, artificial intelligence is like a student who has access to past exam papers and study materials from previous years. Naturally, they’ll breeze through the exam much more easily than someone who only has scattered notes from a few classes.
This is exactly what’s happening in the job market. Some industries have vast amounts of valuable data that AI can learn from, while others are stuck making do with fragmented, patchwork datasets. The numbers speak for themselves: in sectors rich with high-quality data, AI adoption rates could soar to 60%–70%, whereas in industries struggling with data scarcity, the rate might barely reach 25%.
The jobs hit hardest
Software development is facing a major blow. GitHub hosts over 420 million code repositories, with at least 28 million of them publicly accessible—providing millions of examples of programming problem solutions. Tools like GitHub Copilot learn from this vast repository of code, enabling them to write programs independently. Currently, three-quarters of developers are already using AI-powered assistants.
Customer support is also a "live target." Thanks to its wealth of data, this field is perfectly suited for AI automation. IBM notes that AI leverages call, email, and ticket data to enhance response quality while reducing costs by 23.5%.
,,70%
,10%,HIPAA,
,,,
,(FERPA),
,,,AI,,
,“”,,,,500,50
,,——,
,,2030,9200,1.7,,
,:,——,
,,,,
“”:,,
“”,;,,

Agenda ,,
: | :
,
“”