DeepSeek is an open-source AI, which means anyone can download, copy, and build upon it.
Image source:Unsplash/ Google Deepmind
Charlotte Edmond
Senior Writer for the Forum Agenda
DeepSeek has already shaken up the AI industry, surpassing ChatGPT to become the most downloaded free app in the U.S. Apple App Store.
What sets DeepSeek apart is that this Chinese application is open-source—meaning anyone can copy, download, and build upon it.
The World Economic Forum's "AI for Industry Transformation" initiative is exploring the challenges and opportunities within AI-driven innovation.
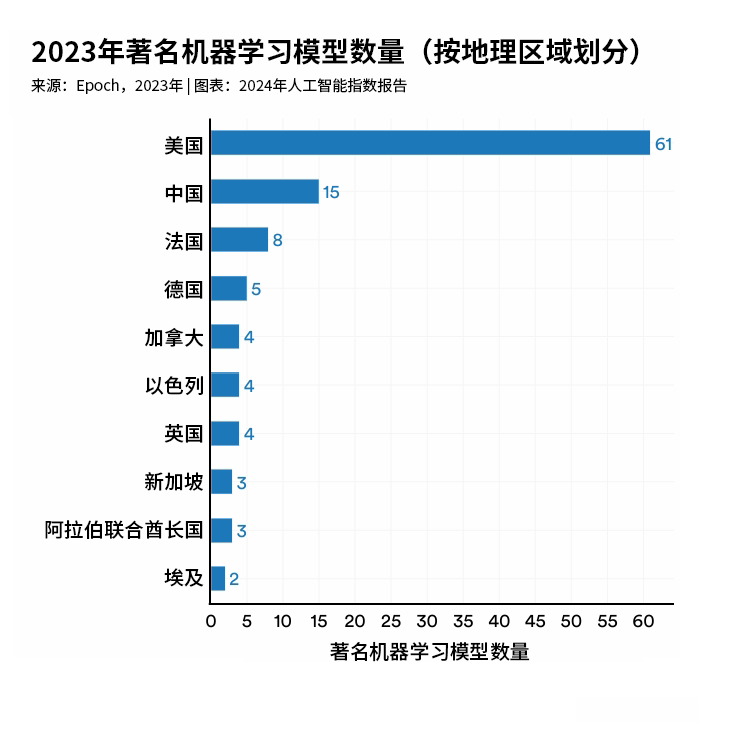
Has artificial intelligence reached its "Sputnik moment"? In other words, has China’s company DeepSeek created a more affordable, energy-efficient, and user-friendly approach to developing AI models?Well-known tech venture capitalist Marc Andreessen thinks so too—he praised DeepSeek as "one of the most stunning and impressive breakthroughs I’ve ever seen, and as open-source technology, it’s a tremendous gift to the world."But what is open-source AI? And why does it represent a significant breakthrough?Why is DeepSeek different?DeepSeek has already shaken up the tech industry's landscape. The UK's Financial Times likened its founder, Liang Wenfeng, to "David" taking on the U.S.'s giant tech behemoths—akin to "Goliath."DeepSeek is headquartered in Hangzhou and was founded in 2023 with investment from the Chinese hedge fund company High Flyer. Its flagship product, the DeepSeek-R1 model, launched in January 2025 and has demonstrated performance on par with other leading AI models in areas like reasoning and mathematical skills. However, its development process differs significantly from that of other AI models in several key ways.Unlike OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Anthropic’s Claude—whose models, datasets, and algorithms are all kept confidential—DeepSeek is open-source, meaning anyone can download, replicate, and build upon it. Its code and comprehensive technical documentation are freely shared, allowing developers and organizations worldwide to access, modify, and deploy the model as they see fit.In contrast, although Meta and Google’s models are open to anyone, they aren’t considered true open-source models because the way users can apply these models is restricted by licensing terms, and their training datasets remain undisclosed.The United States remains the primary source of AI models.
Image source:Stanford University
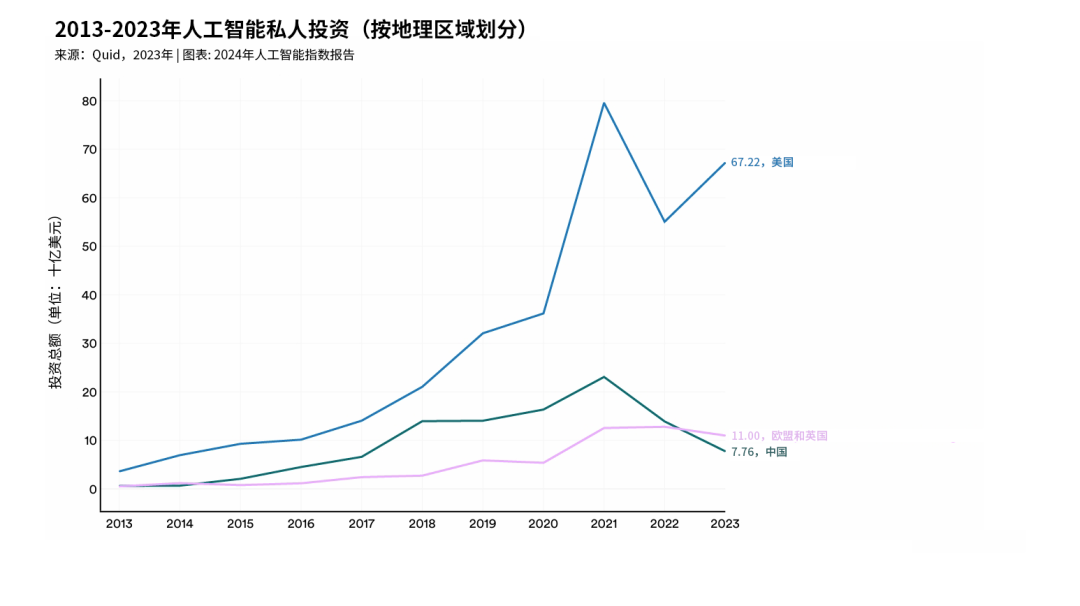
Lower cost, higher energy efficiencyAnother key difference between DeepSeek and other AI models lies in its deployment cost. Data shows that DeepSeek’s setup costs $5.6 million—just 10% of Meta’s Llama model expenses. This naturally raises questions about whether the massive funding demands in the AI market (especially in the U.S.) are as essential as initially thought. As a result, Nvidia, the company designing AI semiconductor technology, saw its stock price plunge significantly at the end of January.If building AI models could be done faster and with lower energy consumption, it would certainly be great news for the environment—after all, the skyrocketing electricity use tied to AI is driving carbon emissions to alarming levels. DeepSeek’s approach offers a more sustainable path toward scaling up artificial intelligence.The United States has invested more in artificial intelligence than the European Union and China combined.
Image source:Stanford University
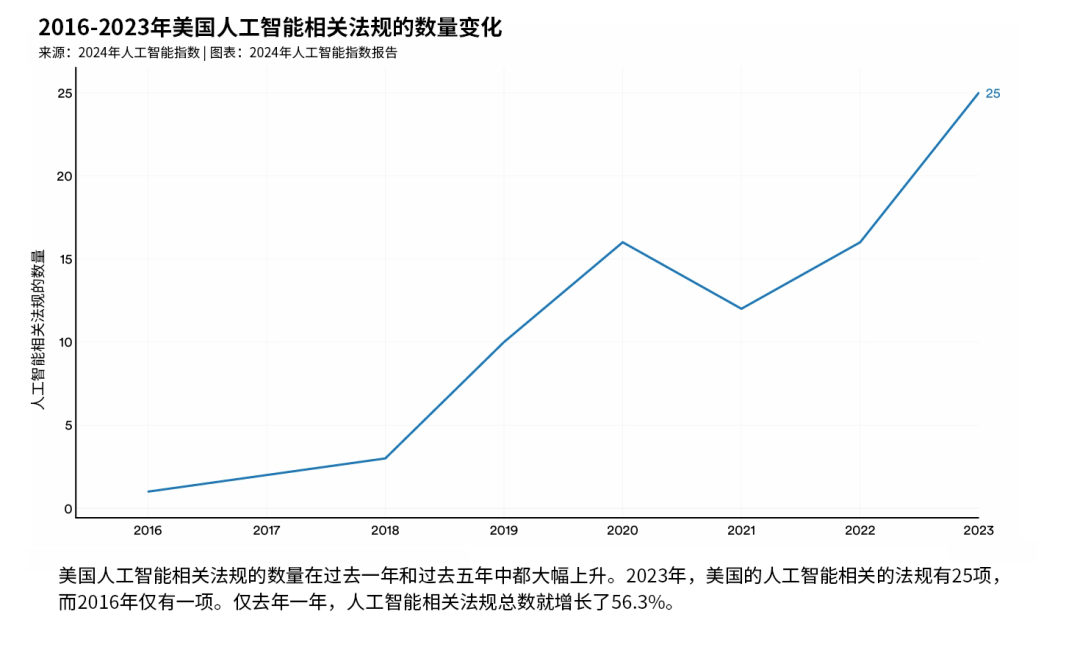
How is open-source AI transforming the market?By the end of January 2025, DeepSeek had surpassed ChatGPT to become the most downloaded free app in the U.S. Apple App Store. Many believe its rapid rise could mark a significant step toward the democratization of AI, empowering small companies, startups, and individual developers to build on top of DeepSeek-R1.Some argue that a more equitable, AI-for-all approach could accelerate innovation in regions where cutting-edge technology is hard to access—and ultimately drive broader technological progress. Instead of focusing on building specialized models, developers could instead channel their resources into crafting tailored applications, unlocking AI's true potential to tackle real-world challenges.This goal is also supported by the World Economic Forum’s “Industry AI Transformation” initiative, which is exploring both the challenges and opportunities brought about by AI-driven innovation—and delves into the transformative potential of AI across industries in its recently released white paper.Many in the tech community believe that DeepSeek's open-source nature fosters a collaborative environment, accelerating AI innovation. Others argue that open-source models may be more trustworthy, as users can inspect the training data themselves.In fact, many leading models have led their companies to face legal lawsuits due to the opacity of their training data.However, DeepSeek has also faced criticism for alleged censorship issues in its responses and training data. Additionally, governments in certain countries have banned the use of DeepSeek, citing privacy concerns. Ensuring transparent data handling, robust security measures, and minimizing unnecessary censorship are crucial for building trust and maximizing technological adoption.The number of AI-related regulations in the United States is rapidly increasing.
Image sourceStanford University
On the other hand, some people believe that open-source AI poses significant risks, as it could be exploited to develop biological weapons or be used maliciously for purposes such as spreading misinformation and fake news.Nevertheless, the emergence of DeepSeek has prompted the AI industry to rethink its approach to competitiveness. Its low-cost, open-source model has challenged conventional wisdom, encouraging countries to reconsider what truly drives success in the age of artificial intelligence.While DeepSeek's open-source framework has fostered inclusivity and transparency, it has also raised critical concerns regarding data privacy, geopolitical dynamics, and security. As the technology continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be essential to unlocking its full potential and ensuring its responsible use.
The above content solely represents the author's personal views.This article is translated from the World Economic Forum's Agenda blog; the Chinese version is for reference purposes only.Feel free to share this in your WeChat Moments; please leave a comment at the end of the article or on our official account if you’d like to republish.
Translated by: Sun Qian | Edited by: Wang Can
The World Economic Forum is an independent and neutral platform dedicated to bringing together diverse perspectives to discuss critical global, regional, and industry-specific issues.
Follow us on Weibo, WeChat Video Accounts, Douyin, and Xiaohongshu!
"World Economic Forum"