Micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises should be actively included in global trade negotiations and policy-making, ensuring that relevant regulations do not impose additional burdens.
Image source:Pexels
Matthew Wilson
Representative and Ambassador of Barbados to the World Trade Organization
Ratnakar Adhikari
Executive Director of the WTO Enhanced Integrated Framework
Small, medium, and micro-sized enterprises face numerous obstacles in global trade, ranging from limited access to financing to complex regulatory requirements across various sectors.
Global initiatives are lowering these barriers by improving trade data, providing targeted financial support, and leveraging digital tools, helping SMEs and micro-enterprises access new markets.
With strong support, SMEs are fully capable of participating in global competition and driving inclusive economic growth.
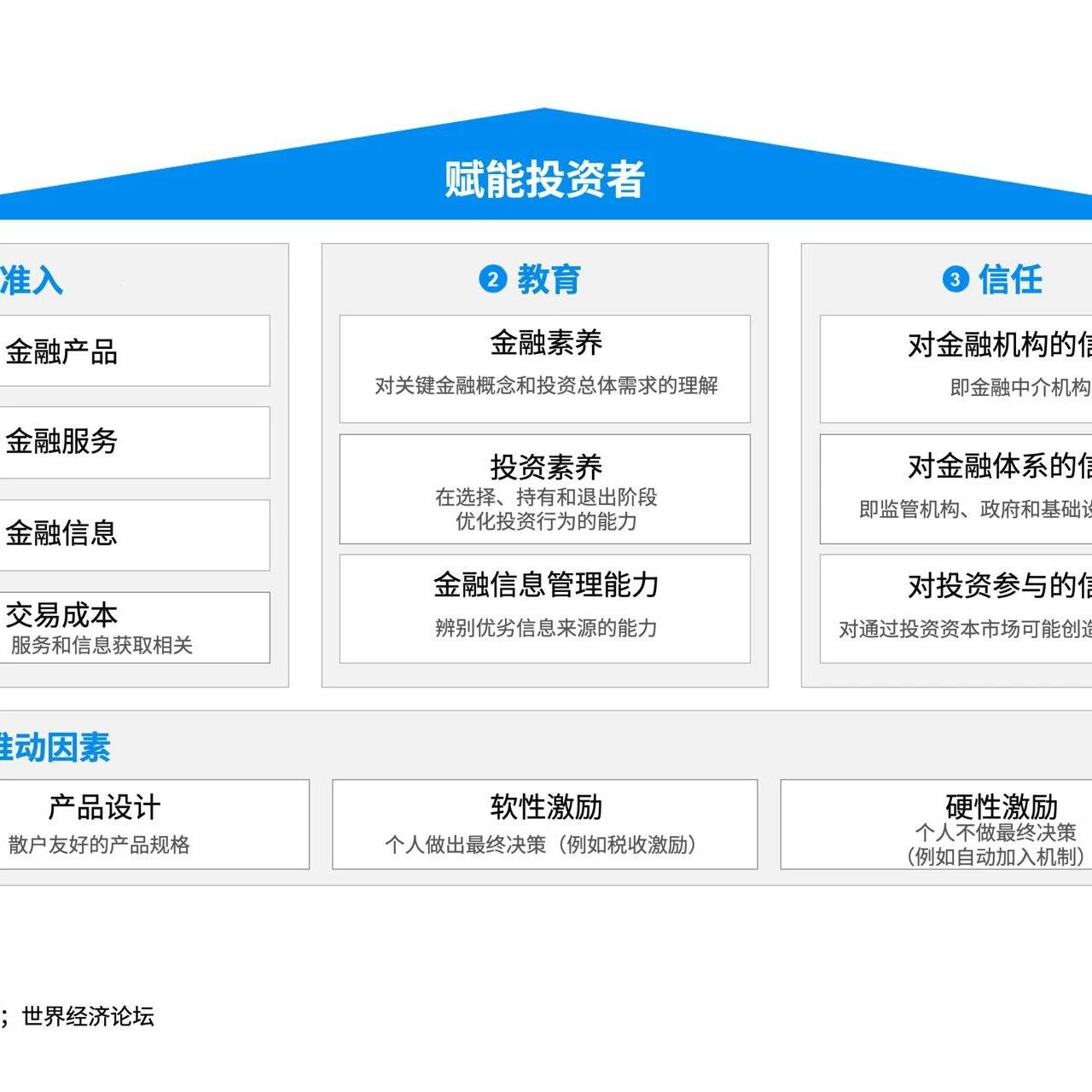
Small, medium, and micro enterprises account forGlobal businesses account for 95% of all companies worldwide and generate 60% of global employment opportunities., is a pillar of the global economy. However,They still face numerous constraints that prevent them from fully benefiting from international trade, such as limited access to financing, complex regulations, and weak digital infrastructure.
Against the backdrop of overlapping crises—ranging from current economic shocks and supply chain disruptions to climate change and geopolitical uncertainties—these challenges are growing increasingly severe.
To address these challenges, international cooperation is essential.Since its launch at the 11th Ministerial Conference of the WTO in 2017,,World Trade Organization (WTO) Working Group on SMEsDedicated to enhancing transparency, expanding trade information channels, and advancing regulatory reforms to encourage the participation of SMEs in global trade.
Meanwhile, other international organizationsIt also provides tailored technical assistance to MSMEs in developing and least developed countries, enhances access to financing, and strengthens their trade capabilities.However, given thatThe Current Multiple Crises, we need to step up efforts to ensure that MSMEs—especially those in the least developed countries—are not left behind.
Eliminating trade barriers for SMEs
Many small, medium, and micro enterprisesLack of resources and capabilities to handle complex international trade rulesThe SME Task Force through“Trade4MSMEs”And “Global Trade HelpdeskPlatform,Providing program guidance and business intelligence to enhance access to information.. The new oneWTO Tariffs and Trade DatabaseIt also provides detailed tariff and import data for SMEs and micro-enterprises, including recent tariff measures taken by WTO members. However, many businesses—especially those in the least developed countries—continue to face barriers due to inconsistent regulations and the high costs associated with trade facilitation.
In practical terms,International Trade Centre (ITC)Significant progress has been made in promoting trade integration among SMEs and micro-enterprises. In 2023 alone, ITC supported over 5,000 SMEs and micro-enterprises in attending trade and market intelligence training sessions, helping more than 2,400 businesses enhance their competitive edge. Notably, nearly 70% of these SMEs and micro-enterprises achieved positive business outcomes.Such as entering new markets or meeting new buyers, etc.
Providing financing for the future of SMEs
Financing challenges are the biggest hurdle MSMEs face as they integrate into the global market.The SME Task Force is dedicated to fostering the exchange of best practices to enhance cross-border payment solutions and financing mechanisms tailored for small businesses. At the 13th WTO Ministerial ConferenceThe SME Task Force also collaborated with the WTO’s Informal Working Group on Trade and Gender Issues to releaseA summary of a financial inclusion initiative aimed at women entrepreneurs,Addressing the specific barriers faced by women
The international financial firm listed in this summary(IFC)Achieved remarkable success in expanding global financing for SMEs and micro-enterprises. In 2023, IFC’s financial clients disbursed $64.4 million in loans to SMEs and micro-enterprises, bringing the total outstanding SME and micro-enterprise loans to $353.2 billion—among which womenLeaderThe company has become a key focus, accounting for nearly 10% of the total loan amount.
Strengthen the Comprehensive Framework(EIF) is addressing the funding gap through targeted support. In Uganda, the government has already incorporated the Enhanced Integrated Framework pilot project into the national budget. The Enhanced Integrated FrameworkSupported Regional Business Services ProgramImproved channels for SMEs and micro-enterprises to access business services and trade-related financial information, enabling businesses to achieveWage growth and job opportunities both on the rise, median wage expenditure increased by more than 100%.
Digitalization: A Factor Shaping the Landscape of SMEs
Digital trade presents tremendous opportunities for SMEs and microenterprises—especially those in the least developed countries—but the digital divide remains a significant challenge. The SME Task Force is actively working to address this issue by focusing on cyber-readiness, electronic document recognition, and paperless trade. The upgradedTrade4MSMEsPlatformMore comprehensive national-level data and over 600 resources,To support SMEs in participating in digital trade.
With support from the Enhanced Integrated Framework, least developed countries are also helping micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises enter export markets. In Senegal, more than 1,600 MSMEs—40% of which are led by women—have joined forces.National E-commerce PlatformCambodian TradeThe portal website has created more than 300 jobs in Cambodia, while South Sudan has launched its first-ever⏤E-commerce Hub, to encourage SMEs and micro-enterprises to participate in digital trade.
Integrating SMEs into global value chains
As SMEs integrate into the global value chain,Still facing challenges such as high compliance costs and barriers to market access.The SME Task Force at "Certified operatorThe project focuses on special regulations tailored for SMEs and micro-enterprises, a proactive move that will benefit small businesses.However, capacity-building in targeted areas still needs to be strengthened.
To amplify the voices of SMEs, the SME Task Force organized a focused conference for small and medium-sized enterprises. At the latest meeting, Ghana-Germany chocolate company FairafricSharedHow it achieves fully localized production in Ghana, and throughInnovative financing approaches to tackle supply chain challengesThe previous meeting also invited small and medium-sized enterprises from countries such as Barbados, Nigeria, and the United Kingdom to participate.
There are also some encouraging examples emerging in agriculture and manufacturing in the least developed countries. In Togo, support from the Enhanced Integrated Framework has helpedIts soybean exports surged from $700,000 in 2015 to $60 million in 2023.AndAttracted more than $250 million in foreign investment,Designed to establish an export-oriented processing industry chain that primarily sources its inputs from small and medium-sized enterprises as well as small farmers.
In Laos,Social enterpriseOck Pop Tok(Meaning "East Meets West") With support from the Enhanced Integrated Framework, we’ve collaborated with over 100 rural women artisans to elevate traditional craft skills and tap into international markets. In Djibouti, formalization efforts have enabled 2,000 SMEs to access financing and trade opportunities, paving the way for their entry into global markets. These examples underscore the critical role of targeted support in enhancing the global competitiveness of SMEs.
Enhancing the resilience of SMEs amid multiple crises
As the world grapples with multiple crises, small, medium, and micro enterprises need more than just survival strategies—they require a supportive environment that fosters resilience and growth. The work of the SME Task Force, alongside strengthened integrated frameworks, the International Trade Centre, and the International Finance Corporation—among other supporting mechanisms—has laid a solid foundation for MSMEs to actively participate in global trade.However, several key efforts are still needed to bridge the remaining gap:
- Strengthening trade policy coordination:Actively include SMEs in trade negotiations and policy-making, ensuring that regulations do not impose additional burdens.
- Scalable Financial Solutions:Building on existing success stories, we will expand trade financing and risk-mitigation mechanisms to help businesses connect with international markets.
- Accelerate the development of digital trade:Invest in e-commerce platforms, digital payments, and cybersecurity to accelerate the adoption and application of digital technologies, while also advancing trade priorities for SMEs and micro-enterprises.
- Continuously advancing capacity building:Continue supporting SMEs in building market connections and preparing for exports,Assisting it in meeting international standards, obtaining certifications, and optimizing trade logistics.
Through these measures, MSMEs—especially those in developing economies and the least developed countries—can become powerful engines driving economic growth, job creation, and sustainable trade. Today, the question is no longer whether we should support MSMEs, but rather how quickly we can implement the scalable solutions they truly need.

The above content solely represents the author's personal views.This article is translated from the World Economic Forum's Agenda blog; the Chinese version is for reference only.Feel free to share this in your WeChat Moments; please leave a comment at the end of the post or on our official account if you’d like to republish.
Editor: Wan Ruxin
The World Economic Forum is an independent and neutral platform dedicated to bringing together diverse perspectives to discuss critical global, regional, and industry-specific issues.
Follow us on Weibo, WeChat Video Accounts, Douyin, and Xiaohongshu!
"World Economic Forum"