
Currently, around 70 nuclear power units are under construction in 15 countries worldwide.
Image source: Reuters/Kai Pfaffenbach
As countries strive to build reliable, secure, affordable, and sustainable energy supplies, nuclear energy is once again coming into the spotlight.
This article presents the global distribution of operating, under-construction, planned, and proposed nuclear power units.
The World Economic Forum's 2025 report, "Driving an Effective Energy Transition," states that nuclear energy—a low-emission power source—is "steadily making a comeback."
Against the backdrop of global efforts to tackle rising energy demands, the climate crisis, and geopolitical uncertainties, nuclear energy is now poised for new growth opportunities.
Currently, there are approximately 440 nuclear reactors operating across 31 countries worldwide, generating about 9% of the global electricity output in 2023.
However, after major accidents like the Chernobyl meltdown in 1986 and the Fukushima nuclear disaster in 2011—both of which cast doubt on its safety—this reliable, low-emission energy source temporarily fell out of favor in many countries. But today, almost every week, we see nations or companies, particularly tech giants, announcing their renewed interest in nuclear power.
This includes the U.S. proposing to "revitalize" its nuclear energy industry, Germany, Japan, and other countries reversing their plans to phase out nuclear power, as well as tech companies signing nuclear power purchase agreements and investing in nuclear energy startups.
So, just how widespread is the impact of this "nuclear renaissance"?
The following diagram shows which countries are currently operating and constructing nuclear power units, as well as those whose units are in the planning phase—meaning they’ve already secured approval, funding, or commitments and are expected to begin operations within the next 15 years—and those in the proposal stage, where specific plans or site selections exist but the exact timeline for commissioning remains uncertain.
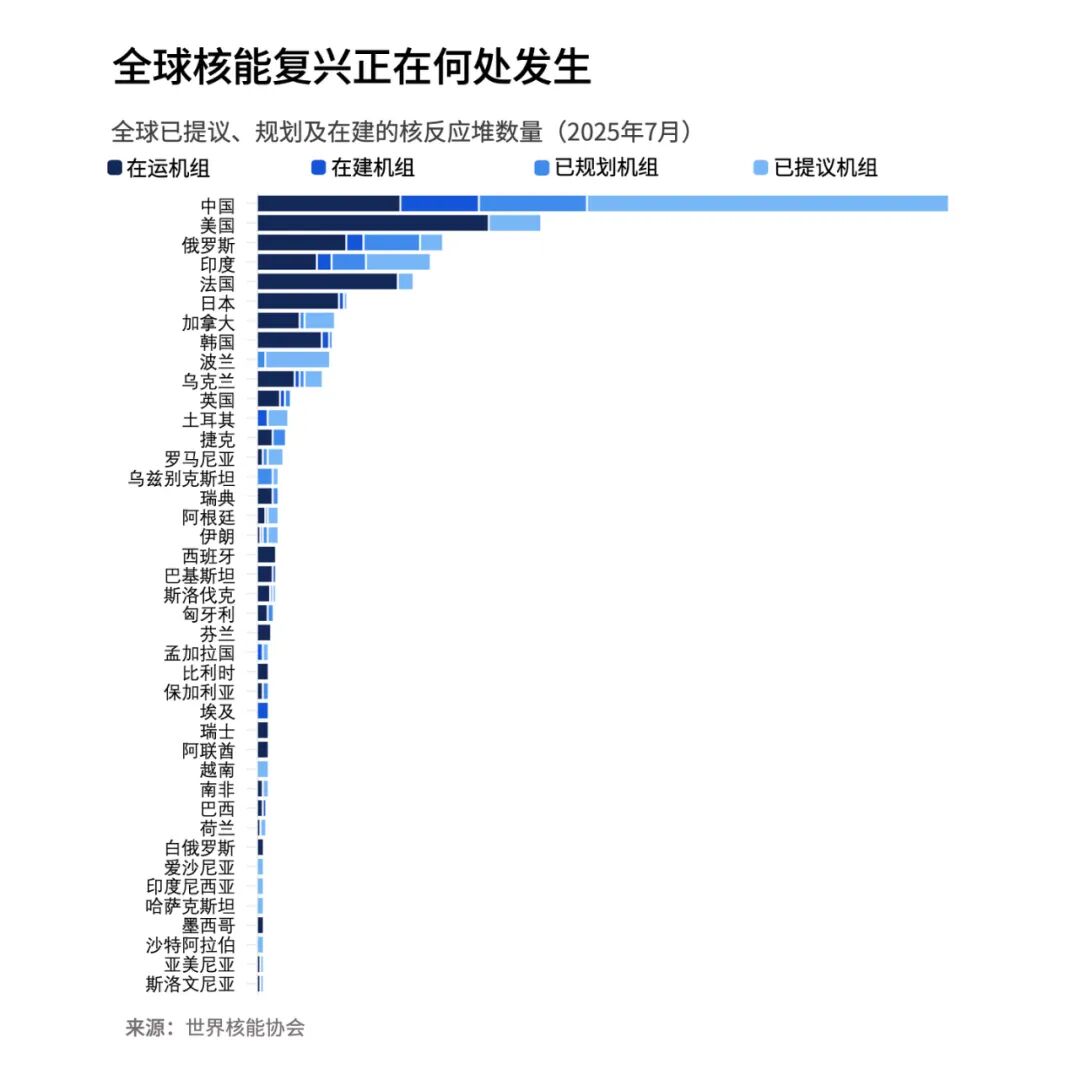
Global Nuclear Power Distribution
Some countries are highly dependent on nuclear energy.
France generates nearly 70% of its electricity from nuclear power, ranking first in the world; Ukraine, Slovakia, and Hungary derive about half of their electricity from nuclear energy.
Nuclear power generation in countries such as China, the United States, Russia, South Korea, and Canada is also quite substantial.
Global Distribution of New and Planned Nuclear Power Plants
Many countries with existing nuclear power projects are now planning or building new nuclear reactor units. Currently, around 70 nuclear reactor units are under construction in 15 countries worldwide.
Developed economies account for more than 70% of the operational nuclear reactors, but emerging economies are steadily increasing their investments in nuclear energy.
As of the end of 2024, about three-quarters of the world's nuclear reactors under construction are located in emerging economies, with half of them in China.
Additionally, around 30 countries are considering, planning, or launching nuclear power projects.
The Importance of Nuclear Energy
At the 2023 COP28 conference, more than 20 countries pledged to at least triple the world’s total nuclear power capacity by 2050. This ambitious goal has already garnered support from hundreds of businesses, major banks and financial institutions, as well as tech giants like Google, Amazon, and Meta.
The World Economic Forum’s 2025 edition of "Driving Effective Energy Transitions" highlights several critical, interconnected priorities: the impacts of the climate crisis; growing energy demand fueled by electrification, soaring air-conditioning usage, and the rapid expansion of artificial intelligence; and global uncertainties—and the resulting pressures on supply chains.
In this context, the report notes that nuclear energy is "steadily making a comeback," a trend driven by both traditional reactor designs and growing interest in small modular reactors. These SMRs can deliver safer, more scalable, and low-carbon baseload power.

The above content represents the author's personal views only.This article is translated from the World Economic Forum's Agenda blog; the Chinese version is for reference purposes only.Feel free to share this in your WeChat Moments; please leave a comment at the end of the article or on our official account if you’d like to republish.
Translated by: Di Chenjing | Edited by: Wang Can
The World Economic Forum is an independent and neutral platform dedicated to bringing together diverse perspectives to discuss critical global, regional, and industry-specific issues.
Follow us on Weibo, WeChat Video Channels, Douyin, and Xiaohongshu!
"World Economic Forum"


