
:Unsplash/Getty Images
Satyanarayana Jeedigunta
Drishti Kumar
,
,,
,
(NASSCOM),650——
,,,,,,
,,,,,,
,
,,AgristackVISTAAR (ADeX) Krishi DSS ,:
VISTAAR(),
AgriStack,:,
,(ADeX)ADeXAgriJSON,39,,
Krishi (Krishi-DSS) (ISRO) ,,
,,
?
,,,,,,
,:(),
1.
- ,,
- ,,
- ,,
2.
- ——
- (DPI),
- API,“”,ADeXAgriJSON,
- ,,
- (DXPs),
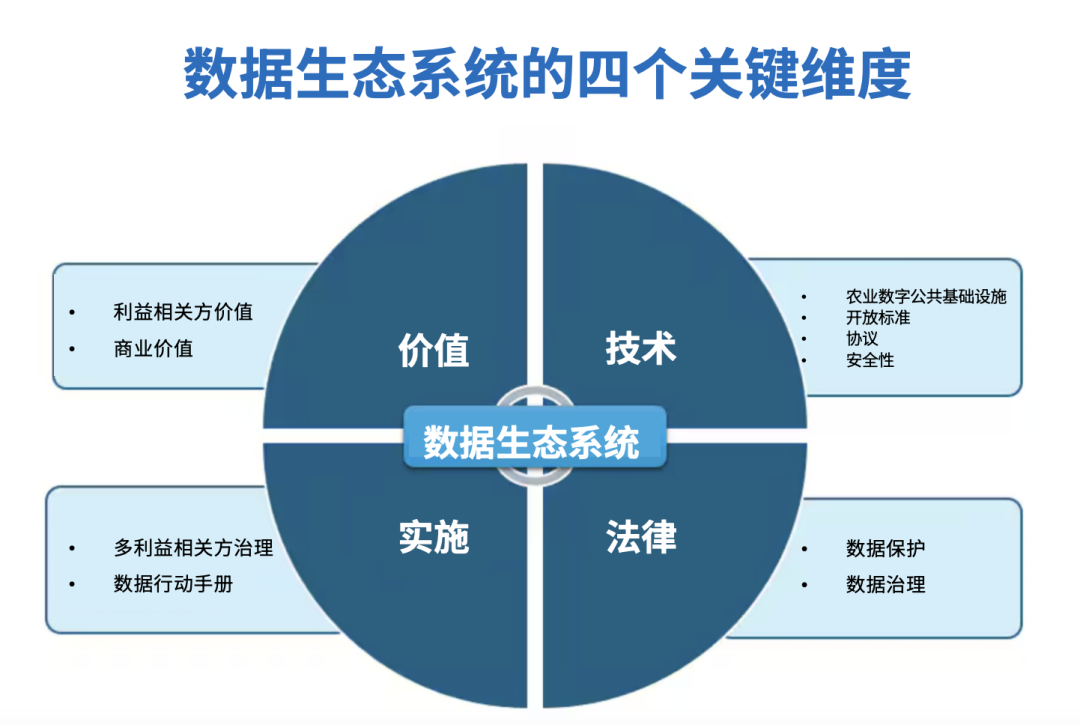
3.
- ,,,,
- ,,(GDPR)(DPDP),
- ,,
4.
- ,
- ,,,
- Implementation partners should assign a dedicated team responsible for the ongoing maintenance and upgrades of the data platform, ensuring that the platform consistently aligns with real-world needs, remains user-centric, and stays in sync with emerging requirements.
- At the same time, standardized implementation guidelines should be developed to provide clear impact assessment methods, enhancing the transparency, consistency, and accountability of project outcomes.
Developing a data ecosystem
The future of digital agriculture in India and other developing countries hinges on the intelligent and strategic application of agricultural data platforms. These platforms not only hold immense potential to fundamentally transform agricultural production methods but also promise widespread global adoption, driving broader, long-term impacts across the entire agricultural system.
However, the platform's visibility alone is not enough to deliver substantial results. The true effectiveness of any data platform hinges on whether it is backed by a tightly integrated, well-designed ecosystem. This requires coordinated efforts from all stakeholders:
- Policy makersPlaying a critical role in shaping forward-looking policies that should be underpinned by fiscal support and regulatory clarity, these policies will drive standardization efforts while fostering innovative development.
- The private sector should take the lead in developing secure, scalable, and interoperable digital infrastructure, laying a robust technological foundation for data-driven agriculture.
- Civil society organizations and research institutions should encourage grassroots adoption and application, foster knowledge sharing, and ensure that technological innovations are truly implemented at the "last mile," while also effectively safeguarding individual rights and interests.
By collaboratively advancing across four key dimensions—value, technology, legality, and implementation—the initiative is poised to establish a data ecosystem that is both resilient and inclusive, ultimately boosting agricultural productivity, strengthening food security, and fostering long-term sustainable development in the agricultural sector.

The above content solely represents the author's personal views.This article is translated from the World Economic Forum's Agenda blog; the Chinese version is for reference purposes only.Feel free to share this in your WeChat Moments; please leave a comment at the end of the post or on our official account if you’d like to republish.
Editor: Wan Ruxin
The World Economic Forum is an independent and neutral platform designed to bring together diverse perspectives to discuss critical global, regional, and industry-specific issues.
Follow us on Weibo, WeChat Video Channels, Douyin, and Xiaohongshu!
"World Economic Forum"


