
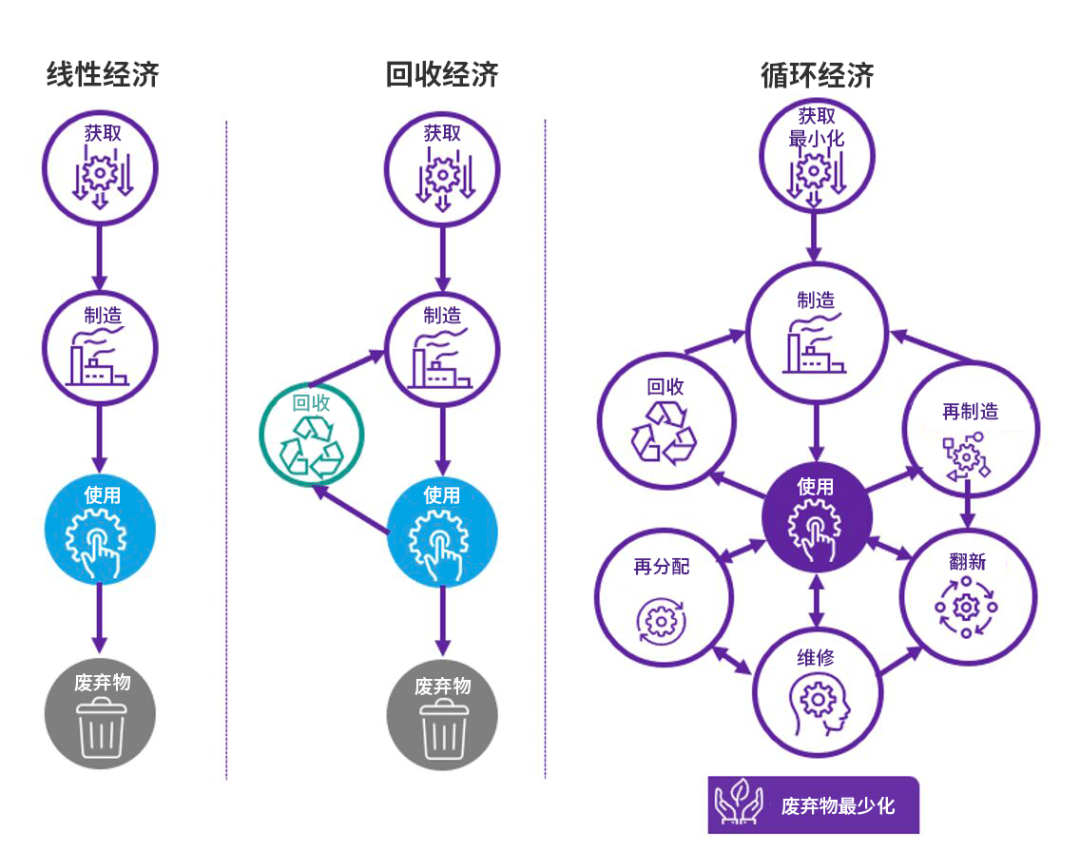
,
Image source:Unsplash/Kilian Seiler
Henrik Hvid Jensen
Chief Technology Strategist at DXC Technology
Developing countries can foster thriving circular economies by nurturing circular economy businesses such as maintenance, refurbishment, remanufacturing, and recycling—creating multiple revenue streams rather than relying solely on the production of new products.
Circular economy practices can create job opportunities in areas such as repair services, parts recycling, and reuse, while reducing reliance on volatile raw material exports and enhancing economic resilience.
Countries that invest in circular economy infrastructure and expertise can become regional hubs for renovation and recycling, attracting multinational investments and ensuring sustained economic growth.
The evolving global legislative and business strategies have also driven profound transformations in manufacturing. Governments worldwide are increasingly enforcing circular economy regulations that mandate product durability, recyclability, and the implementation of extended producer responsibility schemes.
This shift reflects manufacturers' growing endorsement of the circular economy, believing it canCreate more valueAnd with recurring revenue, it can also hedge against the risk of fluctuating raw material prices.
In recent decades, emerging economies such as Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Mexico have become key manufacturing hubs in the global supply chain.
Vietnam has attracted [investors/businesses] thanks to its low labor costs, strategic location, and favorable trade policies.Large-scale foreign investment,In 2023, exports reached approximately $355 billion., primarily targeting developed markets. While this model has fueled economic growth and generated employment opportunities, it has also created a dependency on global demand.
The 5 Major Impacts of the Circular Economy
As the global economy shifts from linear production to circular value creation, developing countries are also beginning to face a fundamental transformation in how value is created, captured, and delivered.
This transformation will reshape existing industrial models, profoundly impacting employment, exports, competitiveness, infrastructure, and skills. For countries aiming to stay competitive in the circular economy and seize new growth opportunities, understanding these effects is essential.
1. Employment Challenges
As demand grows for secondhand and refurbished products, industries reliant on manufacturing new goods may face job losses. For instance, Bangladesh's garment sector accounts for approximately85% of exportsIf consumer spending on secondhand clothing increases, job opportunities in the industry may decline.
2. Declining export revenue
As circular economy practices become increasingly widespread, countries that rely on exporting raw materials or newly manufactured goods may face declining export revenues.
For instance, as metal recycling increases, metal-exporting countries may face declining demand. Similarly, if refurbished, remanufactured, or repaired products gain favor among consumers and businesses, sales in nations that rely on manufacturing and exporting new products could drop.
3. Industrial Competitiveness
Without embracing circular practices, countries that have made significant investments in electronics and textiles could risk losing their competitive edge. Research shows that circular approaches positively impact both total value added and employment.Positive impactProactive transformation can generate economic benefits.
4. Infrastructure and Supply Chain Adjustments
Transitioning to a circular economy requires investing in infrastructure development, including recycling facilities and refurbishment centers. Developing countries may need to restructure their supply chains, which, while challenging, also presents an opportunity.
5.
,,
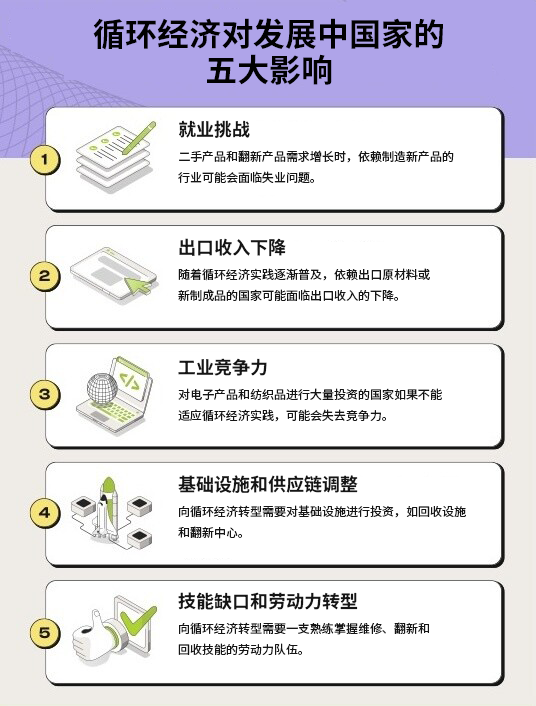
Image source:circularpathwaysbook.com
,,,
1.
,,,
2.
,
,,
3.
“”,,,,
,,,
4.
,()(“”),,
,,,,,
,,,
5.
,
Nhat Tao,,
(EV),,
6.
,,,
,,“”,,,,
,,

Image source:circularpathwaysbook.com
,,
This transformation can drive sustainable economic growth, strengthen industrial resilience, and enhance the position of developing countries in a rapidly evolving global business landscape.

The above content solely represents the author's personal views.This article is translated from the World Economic Forum's Agenda blog; the Chinese version is for reference purposes only.Feel free to share this in your WeChat Moments; please leave a comment at the end of the article or on our official account if you’d like to republish.
Translated by: Sun Qian | Edited by: Wan Ruxin
The World Economic Forum is an independent and neutral platform dedicated to bringing together diverse perspectives to discuss critical global, regional, and industry-specific issues.
Follow us on Weibo, WeChat Video Channels, Douyin, and Xiaohongshu!
"World Economic Forum"


