Zhang Xun
Managing Director, Strategy and Consulting at Accenture
Li Qing
Head of Climate Action, Energy Sector, Greater China, World Economic Forum
In 2023, China added 297.6 gigawatts of new renewable energy capacity, accounting for 63% of the global increase.
China's renewable energy sector accounts for 45.5% of global employment in this industry.
Policy stability, community engagement, and global collaboration are the three key factors behind successful implementation.
China has become a global leader in the deployment of renewable energy.
China has achieved remarkable progress in deploying renewable energy. In 2023, the country added 297.6 gigawatts of new renewable energy capacity, accounting for 63% of the global increase. By 2030, China is expected to contribute 60% of the world’s total new renewable energy installations. As of 2023, China’s renewable energy sector has already created 7.4 million jobs, representing 45.5% of all such employment worldwide.
However, as the scale of renewable energy projects continues to expand, the challenge of aligning the interests of all stakeholders has significantly increased. The traditional linear decision-making model—where governments lead and companies execute—is now struggling to keep pace with the complex demands of large-scale renewable energy initiatives.
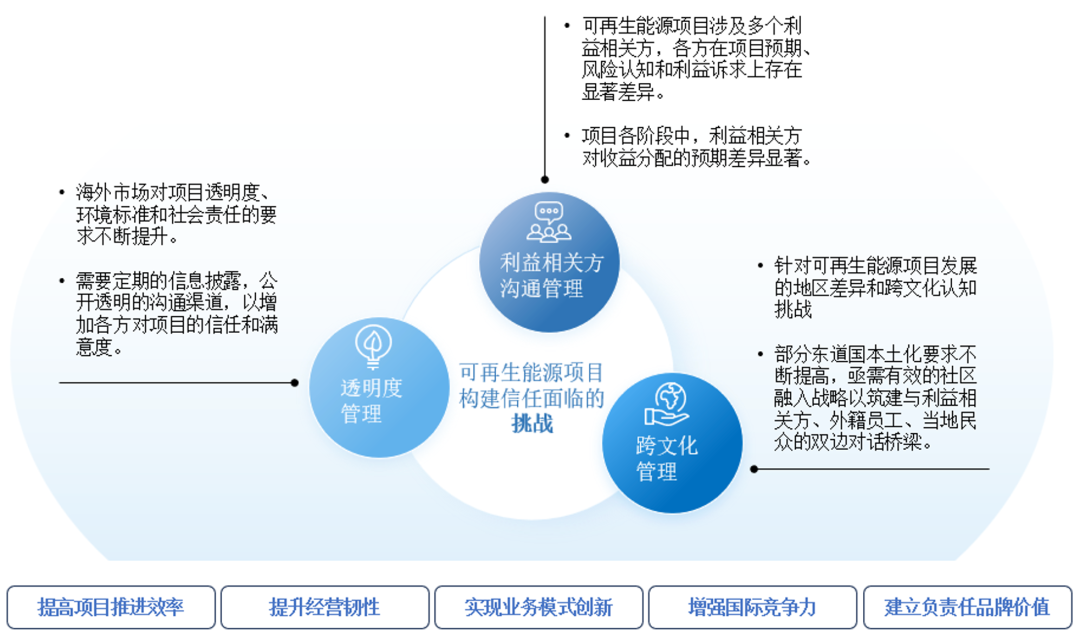
Collaborative Challenges Among Stakeholders in Renewable Energy Projects
Image source: Accenture Analytics
How can multi-party win-win outcomes be achieved through trust-building? China’s practical approach points to three key factors: policy stability, community engagement, and global collaboration. By fostering collaborative partnerships, balancing diverse stakeholder interests, and ensuring the successful implementation of renewable energy projects, we can unlock long-term shared value while driving the responsible growth of the renewable energy sector.
Policy Cornerstone: Stable Expectations and Market-Oriented Reforms
The development of renewable energy requires governments to provide stable, consistent policy support to bolster long-term confidence among all stakeholders. By fostering multi-party collaboration and gradually establishing a mandatory, standardized system for assessing the environmental and social impacts of projects, governments can deliver institutional safeguards for sustainable development.
The Chinese government has long been actively promoting the development of renewable energy. Policies and mechanisms such as the Renewable Energy Law (2006) and the Feed-in Tariff (FIT) have laid a solid foundation for the industry. In recent years, the pace of market-oriented reforms has accelerated, paving the way toward a more competitive and efficient renewable energy sector. Key initiatives like green power certificates and renewable energy trading markets are driving the industry’s transformation. These reforms enable power generators to sell electricity directly to consumers or trade through platform-based systems. Additionally, renewable energy Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) have already been implemented in several pilot projects, exploring long-term contract models. By 2025, China plans to further advance the marketization of renewable energy pricing, gradually reducing reliance on fixed FITs and transitioning to market-driven electricity prices via mechanisms such as green power trading and competitive bidding.
Policy implications: Strengthen regulations for environmental and social impact assessments, strike a balance between policy guidance and market dynamism, and provide investors with long-term confidence.
Corporate Action: Innovative Models and Transparent Commitments
Only by innovating their development models can enterprises earn the trust of stakeholders. By restructuring the value chain, companies can embrace the "Renewable Energy+" development philosophy, driving industrial upgrades while creating shared value. For instance, innovative models like "Wind Power + Tourism" have already been successfully implemented in multiple regions across China, ensuring a clean energy supply while boosting tourism revenue and fostering job growth.
Additionally, transparency is also crucial for renewable energy projects. Renewable energy companies should adopt internationally recognized sustainability frameworks to disclose relevant information and actively participate in globally aligned sustainability assessment systems.
Key initiative: Adopt international standards (such as the ISSB Framework) and participate in the global sustainable development assessment system.
Community Engagement: Sharing Benefits and Bearing Risks Together
Community engagement is the foundation for building trust within the community—and it’s essential for successfully implementing projects and establishing long-term relationships. Involving local residents in project planning and execution not only helps mitigate risks but also enhances efficiency. Businesses can share their benefits with the community through initiatives like community development funds, skills training programs, and job creation efforts.
In China, this type of initiative is already underway. For instance, Pingquan County in Hebei Province has long been renowned for its edible mushroom cultivation industry. By integrating photovoltaic power generation facilities with agricultural production—specifically by setting up edible mushroom farms beneath solar panels—Pingquan County has significantly boosted the efficiency of land resource utilization. This innovative model has led to the development of a 30-megawatt agri-photovoltaic project, providing stable income opportunities for 70 impoverished households and creating employment for more than 200 people.
On the other hand, China's solar energy company LONGi Green Energy has been building a module factory in Dengkil, Selangor, Malaysia, since 2022. To address potential negative impacts the project may have on the local community, LONGi Green Energy has implemented a comprehensive Community Impact Management Plan. This plan focuses on rigorously controlling the movement of construction vehicles, protecting road surfaces, and ensuring both community health and environmental protection. So far, LONGi Green Energy has created approximately 900 local job opportunities, with expectations that this number will grow to 2,000 over the next few years.
Key takeaways: Early involvement in planning, transparent communication, and shared benefits are the core strategies for addressing the "NIMBY effect."
International Collaboration: Jointly Building Standards and Global Mutual Recognition
International organizations play a critical role in building a global trust system. Establishing unified standards for technology, products, and certification is essential for the high-quality development of the renewable energy industry. For instance, the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) has provided a harmonized framework for corporate sustainability reporting, boosting confidence among global investors.
China has also released the "Corporate Sustainability Disclosure Standards—Basic Guidelines," which incorporate topics such as rural revitalization and innovation-driven development. These guidelines serve as a bridge for stakeholders to communicate effectively. Looking ahead, further adoption and enhanced collaboration with global standards will help drive the sustainable growth of renewable energy.
Future direction: Promote mutual recognition of technical standards (such as energy storage certification), align green certificates with carbon markets, and reduce cross-border transaction costs.
Why trust is crucial for the future of renewable energy
As the global energy transition accelerates, the renewable energy industry is entering a new phase. China’s experience demonstrates that renewable energy is not only a technological revolution but also a critical upgrade in societal governance capabilities. To fully leverage scale advantages, we must channel them into collaborative efficiency—fostering multi-stakeholder engagement to resolve conflicts effectively. Meanwhile, market-driven approaches must go hand in hand with accountability, ensuring that short-term profit-seeking doesn’t undermine long-term trust. Finally, local expertise should align seamlessly with global standards, enabling us to embrace an open mindset and strengthen our international voice on the global stage.
To this end, the World Economic Forum’s Center for Energy and Materials has launched the "Responsible Renewable Energy Infrastructure Alliance," developed the "Principles for Responsible Deployment," and established a working group with Chinese stakeholders. This group has identified three key priorities for the responsible development of renewable energy: "Net Zero, Trustworthy, and Circular." These priorities aim to support China’s efforts in building and advancing sustainable renewable energy infrastructure—while also providing valuable insights that can be applied to foster broader industry-wide sustainability.

The above content solely represents the author's personal views.Feel free to share this in your WeChat Moments; please leave a comment at the end of the article or on our official account if you’d like to republish.
Editor: Wang Can
The World Economic Forum is an independent and neutral platform dedicated to bringing together diverse perspectives to discuss critical global, regional, and industry-specific issues.
Follow us on Weibo, WeChat Video Accounts, Douyin, and Xiaohongshu!
"World Economic Forum"